Overview
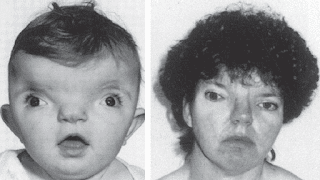
C syndrome, also known as Opitz trigonocephaly syndrome, is characterized by trigonocephaly, severe intellectual disability, hypotonia, variable cardiac defects, redundant (extra folds of) skin, joint and limb abnormalities, and unusual facial features such as upslanted palpebral fissures (upward pointing outside corners of the eyes), epicanthal folds, depressed nasal bridge, and low-set, posteriorly rotated ears. There is evidence of more than one type of inheritance. While many cases are sporadic, autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant, and germline mosaicism have all been suggested. At least some cases of C syndrome have been caused by dysfunction of the CD96 gene.
Symptoms
Symptoms of this disease may start to appear during Pregnancy and as a Newborn.
One of the major features of OTCS is a condition in which the skull is a triangular shape. This occurs due to premature closure of the bones (trigonocephaly or prominent metopic suture due to its premature fusion). Patients with this disorder also have a distinct face in which the nasal bridge is broad with a short nose, there are vertical folds over the inner corners of the eyes (epicanthus) and paralysis of facial muscles (facial palsy). These children may have abnormalities of the outer ear, crossed eyes (strabismus), thin upper lip, smooth vertical groove between the base of the nose and the border of the upper lip (philtrum),an undersized jaw (micrognathia), a short neck and loose skin. Additional characteristics can include abnormalities of the breastbone (sternum), webbed fingers and/or toes (syndactyly), short limbs, heart, pancreas, kidney and lung abnormalities and failure of one or both testicles to move down into the scrotum (cryptorchidism).
Feeding difficulties may occur because of a deeply furrowed palate in the mouth and malposition of teeth. Additional characteristics can include loss of muscle tone and joints in the hands bent in a fixed position or dislocated.
Affected children may have central nervous system malformations and seizures. Developmental delay (motor, mental or global) and speech delay are common and children with C syndrome have intellectual disability that can vary from mild to severe.
Causes
Until recently, OTCS was thought to follow an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. However, it is now believed that the disorder occurs as a result of de novo dominant heritance or gonadal mosaicism. Mosaicism refers to a condition in which a person has cells that differ from each other in genetic makeup.
Dominant genetic disorders occur when only a single copy of an altered gene is necessary to cause a particular disease. The altered gene can be inherited from an affected parent or can be the result of a new change (mutation) in the affected individual. The risk of passing the altered gene from an affected parent to an offspring is 50% for each pregnancy. The risk is the same for males and females.
Diagnosis
OTCS is a clinical diagnosis based on the features mentioned earlier. Since multiple genes (and chromosomal abnormalities) may be associated with this condition, whole exome sequencing (WES) can be used to identify the underlying molecular cause in some patients clinically diagnosed with this condition.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for OTCS but treatment for some symptoms is possible. When trigonocephaly is severe, surgery may be performed to relieve the pressure on the brain and improve facial appearance. Other surgical procedures may be indicated for heart and other malformations. Supportive therapies such as speech therapy and interdisciplinary rehabilitation may be helpful in some patients. Genetic counseling is recommended for patients and their families.
Risk factors
Children diagnosed with MIS-C are often between the ages of 5 and 11 years old. But cases are reported among children ages 1 to 15. A few cases have also happened in older kids and in babies.
Prevention
A vaccine can prevent you or your child from getting or spreading the COVID-19 virus. If you or your child gets COVID-19, a COVID-19 vaccine could prevent you or your child from becoming seriously ill.
To prevent getting the COVID-19 virus and spreading it to others, the CDC recommends following these precautions:
1.Keep hands clean. Wash hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. If soap and water aren't available, use a hand sanitizer that has at least 60% alcohol.
2.Avoid close contact with anyone who is sick. Avoid people who are coughing, sneezing or showing other signs that they might be sick and contagious.
3.In public indoor spaces, keep distance between yourself and others. This is especially important in places with poor airflow.
4.When COVID-19 community levels are high, wear a face mask in public indoor places. If your area has a high number of new COVID-19 cases and people with COVID-19 in the hospital, masks help prevent infection. The CDC suggests wearing the most protective mask possible that you'll wear regularly, fits well and is comfortable.
5.Avoid touching your nose, eyes and mouth. Urge your child to follow your lead and avoid touching the face.
6.Cover your mouth with a tissue or your elbow when you sneeze or cough. Throw away the used tissue. Wash your hands right away.
7.Clean and disinfect high-touch surfaces regularly. This includes areas of your home such as doorknobs, light switches, remotes and keyboards.
TYPE OF DOCTOR DEPARTMENT :-
Comments
Post a Comment