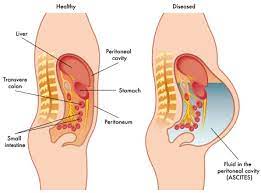
Ascites is a buildup of fluid in the abdomen. This can happen when the liver is not working properly. Fluid fills the space between the organs and abdominal lining, which can cause swelling and pain.
Ascites is a common symptom of cirrhosis, which is scarring on the liver.
As fluid accumulates in the abdomen, a person can feel bloated and uncomfortable. The fluid can also press on the lungs, causing shortness of breath.
Depending on the cause of a person’s ascites, a doctor can treat the condition with lifestyle changes, diuretics, and antibiotics. They may need to drain the fluid with a needle in some cases.
Ascites is the medical term for a buildup of fluid in the abdomen.
It can happen when the blood pressure of the portal vein — which runs from the digestive organs to the liver — gets too high. This increased pressure reduces kidney and liver function, causing fluid to accumulate.
The condition occurs in 80%Trusted Source of people with liver problems or cirrhosis
symptoms
Excess fluid in the abdomen can cause swelling, making the abdomen feel tight and uncomfortable.
The symptoms of ascites can develop over a few weeks or even days. While it may be minor at first, the swelling can become more severe.
Symptoms may include:
- abdominal pain
- bloating
- constipation
- indigestion
- loss of appetite
- frequent urination
- feeling breathless
- fatigue
- back pain
Causes of ascites
Cirrhosis, or liver scarring, is the most common cause of ascites.
Other possible causes include:
- kidney failure
- heart failure
- infection
- pancreatitis
- portal vein thrombosis
- Ascites vs. belly fat
- Although ascites may look similar to belly fat, a doctor will be able to differentiate the two.
Ascites and fat move and feel different. A doctor may examine a person’s abdomen when lying down and standing. The shape of the abdomen may suggest that it contains fluid rather than fat.
A person with ascites may also have a distended abdomen, which is hard and swollen. They may also experience rapid changes in weight and body shape. These changes happen far more quickly than the rate at which a person typically gains body fat mass.
Is ascites life threatening?
In most cases, ascites itself is not life threatening. However, the cause may be a more serious condition that may be life threatening, such as liver failure.
For people who have ascites as a complication of cirrhosis, mortality rangesTrusted Source from 15% in 1 year to 44% in 5 years.
If ascites is left untreated, an individual may have complications. For example, they may develop an infection in the fluid in their abdomen. This can be dangerous if not managed properly.
Treatment and management of ascites
There are a variety of treatments for ascites. A doctor will decide which options are best suited to a person’s condition.
Sodium reduction
A doctor will likely suggestTrusted Source restricting sodium in a person’s diet. In general, they should aim to consume less than 2000 milligrams of sodium per day.
Diuretics
Many people with ascites benefit from diuretics, which are also called water pills. These help rid the body of excess fluid, reducing swelling.
A doctor may prescribe common diuretics such as furosemide (Lasix) and spironolactone (Aldactone).
Paracentesis
Paracentesis is a simple procedure performed by a doctor or medical professional. It involves inserting a needle into to abdomen to remove excess fluid.
If they suspect an infection, a doctor may remove a small fluid sample for testing. However, if a person has a large amount of swelling, a doctor will remove a larger quantity of fluid.
Shunts
A doctor may recommend inserting a shunt to drain the fluid that builds up from ascites.
First, they will numb and clean the area. Then, they will gently insert a long needle down the vein to open it. After making a small incision in the chest area, they will insert a tube that goes from the neck to the abdomen.
Diagnosis of ascites
Diagnosis depends on how much fluid is present in a person’s abdomen. Doctors can often diagnose ascites through physical examination.
They may then confirm the diagnosis using an ultrasound or CT scan of the abdomen.
A doctor will also typically take a sample of the fluid by inserting a small needle through the abdominal wall under local anesthetic, extracting some fluid, and sending it for testing.
Doctors will examine the fluid for signs of cancer and infection to determine the reason for fluid buildup.
Outlook
A person’s outlook depends on the reason for their ascites. If an infection causes a person’s ascites, antibiotics can treat it.
For most people with ascites from cirrhosis, paracentesis and shunts can improve their quality of life. However, they likely will not increase their chances of survival. They instead help manage the condition while a person waits for a liver transplant.
Summary
Ascites is a buildup of fluid in the abdomen. It commonly occurs as a complication of liver disease.
Symptoms include bloating, indigestion, constipation, and shortness of breath. Although it can be treated with medication and simple procedures, it can recur in people with chronic conditions.



Comments
Post a Comment